Theano
Today, the first known woman mathematician and something more. The University of Houston's College of Engineering and the Department of Hispanic Studies present this series about the machines that make our civilization run, and the people whose ingenuity created them.
I was looking into The Pythagoreans the other day when I found an article by María Salmeron about the earliest woman mathematician. In the sixth century BC in Crotona southern Italy lived Pythagoras, the well-known mathematician, and philosopher. We know him well for the theorem that bears his name but, what about his life?
Pythagoras was the founder of a secret society dedicated to study of philosophy and mathematics. Teano was a young disciple, 30 years his junior and one of the brightest within the society. There they met, and even though there've been discussions about their relationship, we believe they married, worked together, and had several children.
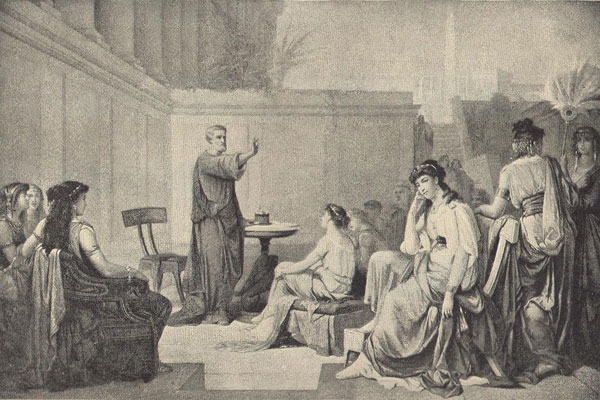

The Pythagoreans followed a strict code of silence
Under the rule of the Pythagorean Society all material property was shared, and knowledge belonged to everyone. Men and women had the same rights and all knowledge was kept in secret. Surely, it was their decision to keep knowledge in secret, what prevents us from finding out about their life and identifying the true authors of the writings they produced.
Even so, several treaties in math, physics and medicine are attributed to Theano including the one on the Golden Section. The number (Φ) PHI, it is a constant proportion — a rectangle with a strange property. If you cut off a square with sides equal to the short side, what's left over is a small rectangle with the same shape as the original one. Ever since Theano, we've looked upon this rectangle as the perfect shape. In nature, the spirals of a mollusk shell and flower petals evolve out of that shape. Architects have based designs on its proportions down through the centuries; it has been used as a mathematical expression of beauty.
Theano's Pythagorean society was an exception, the rest of the Greek society was far from being homogeneous in its acceptance of women. In Athens the presence of women in public meetings was outlawed. Luckily for Theano in Crotona men and women were seen as equals. There were also men like Pythagoras and much later Plato who defended and accepted women as equals in science.

Teano
And so it is that the story of Theano is left behind as well as the acceptance of her contributions by Pythagoras and the other members of the society. Conveniently, their theorems and writings are proven, accepted and studied, but not their philosophy about the feminine contributions.
A revolt against the authority of the Pythagorean society led Pythagoras to suffer a violent death. After the tragedy it was precisely Theano who took charge of the order and spread the mathematical knowledge, and Pythagorean wisdom and doctrines with the help of her children and other members.
So Theano becomes the first known woman mathematician in history. She appears alongside and almost at the same time as Pythagoras who in addition to being the father of mathematics becomes the first feminist mathematician.
I'm Aymara Boggiano, at the University of Houston, where we're interested in the way inventive minds work.
This episode was originally written in Spanish (TEANO) and then translated in English. The references below stem from the original episode and are in Spanish. They are followed by references in English provided by the translator.
Salmerón, María A. "Teano y la ciencia pitagórica." La Ciencia y el Hombre. XXIII.2 (2010)
Figueiras, Lourdes, María Molero, et al. Género y Matemáticas. Madrid: Editorial Síntesis, 1998. 111. (Revista de Divulgación Científica de la Universidad Veracruzana)
The number Phi (Φ)
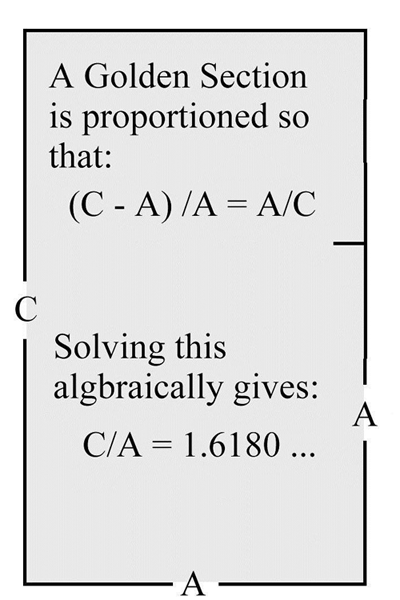
John Lienhard, author of these series offers the above illustration and the following explanation for the Golden Section: "The ratio of sides of the Golden Section rectangle, often noted as Phi (Φ =![]() ), is the difference between the lengths of its sides, along with its short length that would form another rectangle of exactly the same shape."
), is the difference between the lengths of its sides, along with its short length that would form another rectangle of exactly the same shape."
There is a digital copy of the book of Diogenes Laercio, The 8th book: Biography of Pithagoras that can be read here. It contains information about Theano.
There is also a funny explanation of the Golden Proportion in a Disney video: "Donald Duck in the World of Mathematics" it's available in Amazon.
Translator's references:
In Wikipedia see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Golden_ratio
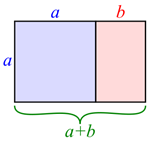 A golden rectangle with longer side a, and shorter side b, when placed adjacent to a square with sides of length a, will produce a similar golden rectangle with longer side a + b and shorter side a. This illustrates the relationship:
A golden rectangle with longer side a, and shorter side b, when placed adjacent to a square with sides of length a, will produce a similar golden rectangle with longer side a + b and shorter side a. This illustrates the relationship:
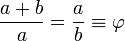
This episode was first aired on June 5, 2012